Description:
Author:
- Marco Romanutti, Saskia Schueler
Sources:
github.com/gephi/gephi-plugins/tree/link-prediction-pluginLicense:
Compatible Gephi versions:
Tools > Pluginsmenu. The following download links may be useful to spread this plugin to people with no internet access, for instance.
README:
Link Prediction
Link-prediction plugin for Gephi, which allows to predict the next edges to be formed using different prediction algorithms. Edges that are added to the network based on the prediction are marked accordingly. Users can limit the number of edges predicted. The plugin contains an evaluation component, which allows to compare the quality of the different algorithms regarding the graph on hand.
The plugin is released under the Apache 2.0 license.
Features
In release 1.3.0 the plugin contains the following functionality:
- Statistics: New edges can be added to an undirected graph using selected algorithms in the
statisticstab. The number of new edges can be specified. In doing so, n new edges are added to the graph iteratively. The calculation of the next predicted edge is always based on the graph of the preceding iteration step. - Filter: The added edges can be displayed by means of filters. On the one hand, the corresponding algorithm is specified as the filter criterion. On the other hand, the number of added edges can also be restricted.
- Evaluation: Based on an initial graph and a validation graph the accuracy of the link predictions using different algorithms are evaluated. Besides the final accuracy, the generated report also shows the accuracy after each iteration step.
Get started
Run Gephi with installed plugin
If you checked out the sources via Maven, you can run Gephi with your plugin pre-installed using the following command. Make sure to run mvn package beforehand to rebuild.
mvn org.gephi:gephi-maven-plugin:run
If you downloaded the plugin distribution files (*.nbm) you can just navigate to Tools > Plugins > Downloaded and add the Plugin there.
Predict new edges
To predict new edges, run a new link prediction using Statistics > Edge Overview > Link Predictions.
The number of new edges can be specified. In doing so, n new edges are added to the graph iteratively. The calculation of the next predicted edge is always based on the graph of the preceding iteration step.
Information to the newly added edges are visible in the following columns under Data Laboratory > Edges :
- Chosen link prediction algorithm: Algorithm that was used to predict the edge.
- Added in run: Iteration, in which the edge was added.
- Last link prediction value: Calculated link prediction value according to the used algorithm. The values are not normalized.
Filter predictions
The filters under Filters > Link Prediction then allow you to narrow down the corresponding edges.
Edges can be filtered according to the algorithms with which they were added.
Furthermore, the number of added edges can also be restricted to the first n added edges.
Evaluate prediction algorithms
The evaluation can be run using Statistics > Edge Overview > Eval. Link Predictions Algorithms.
Starting with an initial graph
at time t we predict n edges
which results in a Graph
at time t + n.
For each algorithm a new workspace is created which is used to apply the predictions. The initial and validation graph are therefore not changed.
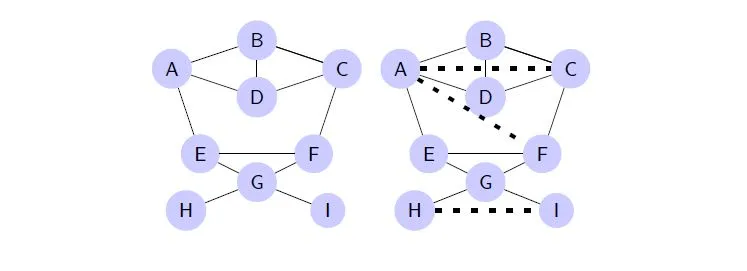
The following figure shows the graphs
(on the left) and
(on the right):

To evaluate their accuracy using a validation graph
and its additional edges
at time t+n are used. In comparison to the Graph
this graph additionally contains the edges
,
and
:

The accuracy then is calculated as percentage of the correct predicted edges. In the current implementation, the results are rounded to two places.
In the above example of three additional edges the edges
and
were predicted correctly. Therefore an accuracy of 66.67% is achieved:
Algorithms
Link prediction is based on an existing network and attempts to predict new edges. The most popular application is the suggestion of new friends on social networking platforms.
To predict a new edge, different algorithms exist. The plugin allows to easily add new algorithms. Currently, the algorithms common neighbours and preferential attachment are implemented. To show the functionality of the algorithms, the following example graph is used:

Common neighbours
Common neighbours calculates for two unconnected nodes how many common neighbours exist. The higher the calculated value, the more likely a new edge will be added between the two nodes.
The following formula represents, how the number of common neighbours of two nodes
and
can be calculated. The call to the function
returns all neighbours of a node in a set, e.g.
returns all neighbour nodes of node
.
Applied to the above example graph, the common neighbour algorithm would predict a new edge between nodes
and
.
The following examples show some of the calculated values:
The current implementation of the algorithm has a complexity class of .
Preferential attachment
The basic assumption with Preferential Attachment is that the probability that a node is affected by a newly added edge, is just proportional to the number of neighbours. The more neighbours a node has, the larger the likelihood that it will be affected.
To calculate preferential attachment, the number of neighbours of both nodes are multiplied by each other. The call to the function
returns again all neighbours of a node in a set, e.g.
returns all neighbours of node
.
Applied to the above example graph, preferential attachment would predict an edge between node
and
and calculate the following values:
The implementation of the preferential attachment algorithm is of complexity class .
Limitations
With the limitations of the implemented algorithms, only undirected, unweighted graphs are supported currently.
The plugin was tested using graphs with less than a thousand nodes. Link predictions in larger networks can lead to long runtimes.